Cryptography Architecture
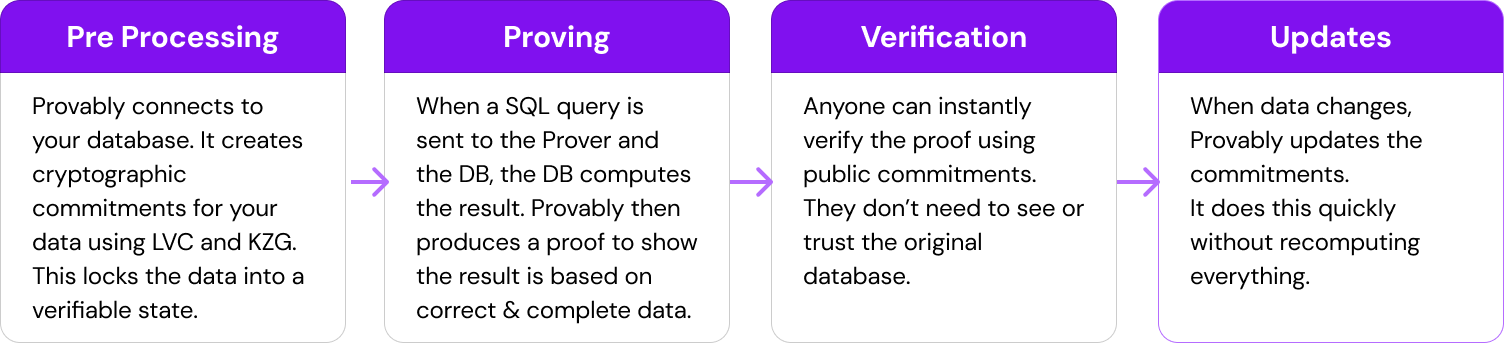
Database Setup phase: using the cryptographic public keys computed by a trusted ‘powers of tau’ setup ceremony, the Prover commits the data stored in the database using LVC and KZG commitment schemes. Data commitments are public and may also be computed by the data sources that ship them to the Prover along with the data.
Query Proof Computation phase: after the storage server has computed the query’s result, the Prover computes a corresponding proof using (i) the LVC vector commitments of the elements included in the answer, in order to prove answer’s correctness; (ii) the set accumulators based on the KZG polynomial commitment scheme, in order to prove answer’s completeness.
Query Proof Verification phase: Once the Verifier has received the query’s answer, the corresponding proof and it has accessed the public data commitments, it separately checks the vector commitments and the set accumulators. If both checks pass, then the query’s answer is verified.
Update Setup phase: Commitments computed during the database setup phase can be updated to include new data from the database. Specifically, using cryptographic public keys, the Prover or data sources can update the LVC vector commitment to include new data or update specific positions with new values. This avoids recomputing the setup phase in its entirety, making the process more efficient.